C. nippodorsalis Sasa 1979
as new name for Chironomus strenzkei sensu Sasa 1978 (name preoccupied)
Syn: Chironomus inaabeus Sasa, Kitami and Suzuki 2001 (Yamamoto and Yamamoto 2018)
Considered a synonym of C. alpestris to which it is obviously closely related, but M. Yamamoto has noted some differences in the larva, and there is at least one different sequence in the polytene chromosomes and a number of different base pairs in the Barcode sequence (see below).
In BOLD Bin: BOLD:AAW4001.
Same bin as C. alpestris
Adult
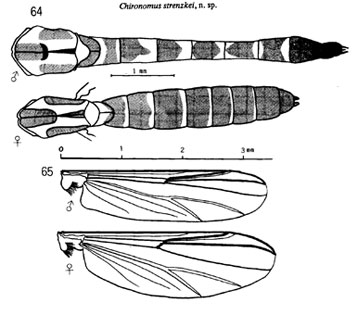 Male: Wing length 3.40-3.60 mm, width, 0.82 mm. VR 1.08. AR 2.96-3.1. BR 2.0
Male: Wing length 3.40-3.60 mm, width, 0.82 mm. VR 1.08. AR 2.96-3.1. BR 2.0
Coloration generally brown to yellow, with dark brown markings on thorax and abdomen. Vittae almost uniformly dark brown; scutellum yellowish brown, postnotum dark brown.
Head: Frontal tubercles small, abt 18-24 µm. 26 clypeal setae.
Palps (microns) (segs II-IV): 90 : 250 : 260 : 390 (Sasa 1978
Indian specimens: 55 ; 53 : 215 : 230 : 275.
Thoracic setae: Achrostichal - at least 9; Dorsolateral - 21-22; Prealar 8;
Supra-alar - 1; Scutellar in two rows - anterior 8, posterior 14.
Legs with dark knees, tibia and tarsi; no beard.
Proportions (micron):
|
Fe
|
Ti
|
Ta1
|
Ta2
|
Ta3
|
Ta4
|
Ta5
|
LR
|
F/T
|
BR
|
PI
|
1330
|
1140
|
1860
|
900
|
790
|
650
|
280
|
1.63-1.75
|
1.17-1.18
|
2.0-2.6
|
PII
|
1410
|
1285
|
780
|
420
|
300
|
190
|
145
|
0.60-0.61
|
1.10-1.11
|
|
PIII
|
1570
|
1570
|
1050
|
600
|
440
|
280
|
160
|
0.67-0.72
|
1.00-1.03
|
|
About 5 setae on tergite IX. Hypopygium: Anal point slender, expanded distally; The superior volsella is a little 'beak-like' (S-type of Strenzke 1959), but beak is quite short; about 5 setae central on tergite IX.
Female: Coloration generally as in male, except that the abdominal segments do not have the the conspicuous pale bands. Thoracic ground color grey, with vittae black or dark brown, scutellum brown, postnotum nearly black. Leg coloration as in male. Abdominal tergites almost entirely black.
Wing length 3.6 mm, width 1.1 mm.
Antennal proportions (micron): 110 : 110 : 130 : 130 : 240. AR 0.5; A5/A1 2.18. Frontal tubercles small 15 µm long and 13 µm wide.
Palp proportions (segs 2-5) (micron): 60 : 220 : 240 : 350 .
Leg proportions (micron):
|
Fe
|
Ti
|
Ta1
|
Ta2
|
Ta3
|
Ta4
|
Ta5
|
LR
|
F/T
|
Ta4/Ti
|
PI
|
1830
|
1440
|
2760
|
1420
|
1320
|
1270
|
450
|
1.92
|
1.27
|
0.31
|
PII
|
1810
|
1730
|
1000
|
540
|
390
|
220
|
190
|
0.58
|
1.05
|
|
PIII
|
2030
|
2030
|
1440
|
810
|
630
|
370
|
210
|
0.71
|
1.00
|
|
Pupa: Sasa notes only that the spurs of segment VIII have 3-4 spines.
Fourth instar larva: A medium plumosus-type. Ventral tubules relatively long, anterior with elbows, posterior pair coiled.
Head capsule relatively long and narrow, mentum relatively narrow, mentum width/VHL about 0.49-0.52. Gular region darkened to the width of the mentum, over posterior two thirds; frontoclypeus dark, also darkened outside clypeus. Clypeal chaetae smooth in outline; clypeal aperture about 3.14-3.75 times longer than wide.
Mentum (Fig. a) with 4th laterals reduced to about the level of 5th laterals (type II), 1st laterls tending to curve outwards; central trifid tooth with c2 teeth well separated (type III).
Ventromental plates (Fig. c) separated by about 0.40 of the mentum width, with about 35-37 striae. Pecten epipharyngis with about 12-14 long pointed teeth (type A), when not worn.
Premandible with sharp teeth, the outer tooth longer; inner tooth about 1.5 to 2 times wider than outer tooth.
Antenna (Fig. d) with basal segment about 3.2-3.4 times longer than wide, ring organ about half way up from base; AR about 2-2.15, A3 quite short; segment proportions (microns) 110 : 30 : 7 : 11 : 6.
Distance between antennal bases may be greater than or about equal to that between the S4 setae, which are separated by 0.75 of the mentum width; dorsal RO very slightly posterior to S5 setae.
Mandible (Fig. b) with 3rd inner tooth well developed but only moderately colored (Type IIIB; about 18-20 furrows on the outer surface at the base; 10-12 taeniae in Pecten mandibularis; MTR 0.28-0.36.
Cytology: Four polytene chromosomes with the pseodothummi arm combination AE, BF, CD, G.
Nucleolus subterminal in arm G, which is closely paired and has three BRs, the largest about a third from the distal end. No nucleoli in other chromosomes.
No chromosomal polymorphism in the five larvae investigated.
Differs from C. alpestris by a ccomplex inversion in arm E.
NidA1: 1 - 2c, 4 - 9, 2d -3, 12 -10a, 13 - 19 (as alpestris)
NidB1: not mapped. Puff (group 7?) about a third from the distal end. (as alpestris?)
NidC1: possibly 1 - 2f, 11c - 10, 16 - 17a, 6 -2g, 11d - 15, 9 - 7, 17b - 22 (as alpestris?)
NidD1: possibly 1a(b), 17d - 19d, 10d - 1c(b), 17c - 10e, 19e - 24g (as alpestris?)
NidE1: 1 - 2c, 8b - 6, 3 - 2d, 8 - 9, 4 - 5, 12a - 10, 12b - 13 i.e. In5-9 and In9-3 from alpestris
NidF1: 1 - 10, 15 - 11, 16 - 23 (as halophilus, alpestris)
NidG1: The three BRs are in the distal part of the arm. (as alpestris)
Found: India - Jammu & Kashmir: Kabeer colony, Jammu; Deoli Village.
Also found in Israel - Mt. Hermon.
Yamamoto and Yamamoto consider C. nippodorsalis differs from C. alpestris in the length of the Ventral tubules (about equal in C. alpestris but anterior pair much longer in C. nippodorsalis. As well, the labral chaetae, which are serrated on the anterior portion in other species, are quite smooth in C. nippodorsalis (Yamamoto, pers. comm.).
Molecular
MtCOI sequence from Chironomus nippodorsalis, C. dorsalis sensu Strenzke 1959 and C. alpestris is in GenBank and the BOLD databases (where all are in the same BIN). However, the identification of many specimens is dubious.
[ Return to Index
| Go to C. alpestris ]
|
