| Fe
| Ti
| Ta1
| Ta2
| Ta3
| Ta4
| Ta5
| LR
| F/T
| BR
|
PI
| 1560
| 1500
| 1925
| 1210
| 845
| 665
| 315
| 1.23-1.35
| 1.03-1.05
| 3-6 & 6-9
|
PII
| 1680
| 1685
| 945
| 620
| 480
| 460
| 230
| 0.55-0.57
| 0.96-1.02
| -
|
PIII
| 2050
| 2150
| 1385
| 910
| 680
| 440
| 260
| 0.63-0.65
| 0.94-0.98
|
|
Abdominal tergites with a broad dark band covering most of the surface, leaving only a narrow pale band at the posterior edge. About 11.5 (8-15) setae, probably in barely visible individual spots in a large pale patch on TIX.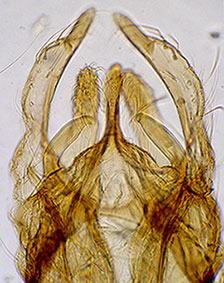
Anal point narrow at the base, slightly expanded at distal end, reaching about 2/3 along the length of the gonostylus. Superior volsella of E-type (between h and i) of Strenzke (1959); Inferior volsella reaching almost to end of anal point, with simple seta. Gonostylus moderately swollen, narrowing over posterior third, sometimes relatively sharply.
Female
Based on one specimen (with LR from a second specimen).
Wing length abt 4.4 mm, width abt 1.2 mm, VR abt 1.06; 4 SCf on brachiolum; 17-20 setae in squamal fringe.
Head: Frontal tubercles about 38 x 10 micron (3.75 times longer than wide); antennal segments (micron) 211(0.41) : 136(0.56) : 141(0.45) : 146(0.53) : 221 ; AR abt 0.35; A5/A1 abt 1.05. Abt 41 clypeal setae; Palpal proportions (micron) 65.5 : 80 : 231 : 291 : 432; P5/P4 1.48; P5/P3 1.87.
Setae: 18-19 Acrostichals; 22 Humerals+Dorsocentrals; abt 6 Prealar; 1 Supra-alar; 33 Scutellar in two rows (ant row abt 18, post row abt 15 larger setae).
BR 1.35. Leg lengths (microns) and proportions:
| Fe
| Ti
| Ta1
| Ta2
| Ta3
| Ta4
| Ta5
| LR
| F/T
| Ta4/Ti
|
PI
| 1635
| 1445
| 1960
| 1040
| 785
| 610
| 315
| 1.36-1.38
| 1.13
| 0.31
|
PII
| 1645
| 1570
| 885
| 495
| 365
| 255
| 190
| 0.56
| 1.05
| -
|
PIII
| 1875
| 1875
| 1230
| 735
| 570
| 470
| 230
| 0.66
| 1.00
|
|
Abdomen generally brown. No information for segment X or the cerci.
Pupa: Length about 11.8 (10.2-12.5) mm (males 12.0 & 12.5 mm), inner margin of wing case about 2.29 (2-2.45) mm (males).
Cephalothorax and abdomen yellow-brown. Cephalic tubercle about 133.5 (106-160) (106-134 x 75 µm, male); 134-160 µm (female), with sub-apical seta about 65-78 µm (male), 78-88 µm (female); and slight indication of a frontal wart.
Respiratory base about 181.5 (158-205) µm long 71 (62-80) µm wide, HR 2.55-2.56, base of respiratory filaments almost divided in middle. Muscle scars on abdominal tergites slightly darkened; about 65-100 recurved hooks on abdominal segment II, occupying about 59-67% of segment width. Pedes spurii A of segment IV about 258 (215-301) x 201.5 (180-223) µm (0.23 (0.20-0.26) of the length of segment IV).
Posterolateral spurs of segment VIII with numerous spines 18.8 (17-22) spreading out like a hand with the fingers spread.
About 111.75 (107-115) taeniae on each side of the anal lobe, mostly in a single row. Shagreen thickest in the centre third of the posterior 2/3 of segments II-IV and spreading laterally at the posterior margin; wider and further anterior on seg. V and essentially reduced to 2 small patches around the posterior setae of segment VI; little on VII-IX.
Larval Morphology: a salinarius-type larva. Largest NZ species, length about 15.3-21.5 mm (female), 15.3-18.7 mm (male). Anal tubules short and often tending to a point.
Head capsule with frontoclypeus and most of the gular region very dark.
Most distinctive feature is the high number of striae (75-99) on the Ventromental plate.
Mentum of type II (i.e 4th laterals reduced at least to the level of 5th laterals) with central trifid tooth of Type II, although sometimes the c2 teeth are less separated from the c1 tooth.
Pecten epipharyngis with about 12-15 relatively sharp teeth, some reduced. Premandible with the two blades about equal in length, inner blade about twice the width of the outer (2.0-2.5).
Antennal segments in proportions (micron) 163 : 37 : 8 : 15 : 8 ; AR 2.0-2.3; basal segment of antenna relatively long and narrow, about 3.1-3.7 times as long as wide.
Mandible with 3rd inner tooth darkened and often fully separate (i.e. Type IIIC); about 17-23 striae on the outer surface near the base.
Cytology: 3 polytene chromosomes, modified pseudothummi-complex arm combination (BF,CD,GEA).
Three nucleoli, one in arm G, one proximal and another medial in arm F(Lentzios & Stocker, 1979). The medial nucleolus may not always be developed, since Lentzios & Stocker (1979) did not find it in their material.
zeaA1 differing from oppositus A4 sequence by a simple inversion 11-2e; arm E pattern not typical but zeaE1 appears to differ by a small inversion 5c-7 from oppositus E1. Arm F differs from that of novae-zelandiae, etc., by inversion of the region 7 to 11.
Considerable polymorphism in arms A, B,C, E, and G(?); sex determiner in arm C, probably near the centromere (Martin & Lee, 1984).
Lentzios et a. (1980) give some information on the number and location of C-bands.
zeaA1: 1a-e, 2g - 3, 1f - 2e, 10 - 11, 2f-d, 8 - 9, 3f-i, 12c-a, 4 - 7, 13 - 19
hypoth: 1a-e, 2g - 3, 4a, 12a-c, 3i-f, 9 - 8, 2d-f, 11 - 10, 2e - 1f, 3e-b, 4b - 7, 13 - 19
zeaA2: 1a-c, 10 - 11, 2f-d, 8 - 9, 3f-i, 12c-a, 4a, 3a - 2g, 1ed, 2e - 1f, 3e-b, 4b - 7, 13 - 19
zeaB1: Puff, with proximal dark bands (groups 7 and 8), in proximal third of arm.
zeaB2: Inversion of distal end of arm, distal to large puff.
zeaC1:
zeaC2: Inversion of about 2/3 of arm.
zeaD1: 1-2, 16-13, 18, 5-3e, 10a-c, 6-9, 3d-a, 10d-12, 19-24
zeaE1: (approx) 1?- 3e, 10b - 8, 5c - 7, 5b - 3f, 10c - 13
zeaE2: (approx) 1?-f, 4b - 5b, 7 - 5c, 8 - 10b, 3e - 2, 4a - 3f, 10c - 13
zeaE3: (approx) 1?- 3e, 10b - 8, 5c - 7, 5b - 3f, 10c-g, 12 -11, 13
zeaF1: 1 - 2a, 10 - 8, 11 - 15c, 2c - 7, 2b, 15d - 23 (In7 - 11 from oppositus F3)
zeaG1: fused to arm E.
zeaG2: possible inversion
Molecular:
MtCOI - GenBank (AF192209.1) and sequences in BOLD Bin: BOLD AAS1265 (see above)
gb2Β - GenBank (AJ003813)
gb9 - GenBank (AJ003814.1)
Known Localities
This appears to have been the "salinarius-type" studied by Robb (1966). It is referred to as C. zealandicus Type 2 by Lentzios & Stocker (1979) and Lentzios et al. (1980), who received their material from Lake Okaro.
Martin (1998) gives some information and drawings of immature stages.
[ Return to Key| Go to References ]