Abdomen with a band across the middle of the anterior tergites, which expands posteriorly on segments V-VIII; about 6.2 (4-7) setae in several pale areas on tergite IX.
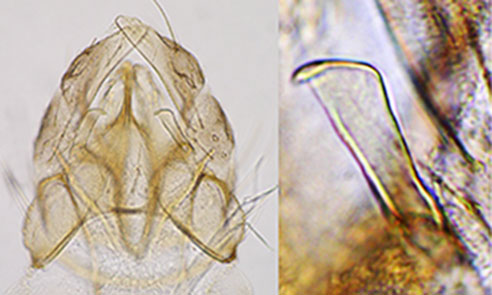
Male hypopygium (left) and SVo (right) of C. kangleipak/
Superior Volsella variable (mounting variants?) mostly E type of Strenzke (1959); Inferior Volsella with simple setae, reaching to end of anal point which is darkened and broadened at tip. Gonostylus somewhat swollen proximally and tapering sharply over posterior third to quarter.
Female
Wing length 3.2 (2.35-3.85) mm, width 0.62-0.81 mm; about 10.7 (8-15) setae on squamal fringe, abt 2-3 SCf on brachiolum. VR 0.89-0.93.
Head: Frontal tubercles small, about 20 (15-25) µm and 1.1-1.3 times longer than wide. Antennal segment lengths (micron) 181 : 110 : 126 : 122 : 206; necks of segs 2-4 comprising 0.35, 0.28 and 0.4 of the segment length, respectively; AR about 0.38 (0.37-0.39), and A5/A1 1.14 (1.05-1.18).
Palpal proportions (µm) 56 : 66 : 170 :185 : 300; P5/P4 1.4-1.62, P5/P3 1.45-1.75.
Clypeal width about 1.3-1.6 times that of the antennal pedicel, about 26 (24-29) clypeal setae.
Thoracic setae: about 13 (10-20) acrostichal; 2-5 humeral (roughly linear or in small group), 11 (10-12) dorsocentral, (14.3, 12-17 dorsocentral+ humeral); 4-5 prealar; 1 supra-alar; 2 in anterior row, at least 9 in posterior row (total 11-13) on scutellum.
Leg lengths and proportions (micron):
|
Fe
|
Ti
|
Ta1
|
Ta2
|
Ta3
|
Ta4
|
Ta5
|
LR
|
F/T
|
Ta4/Ti
|
PI
|
1225
|
1070
|
1805
|
890
|
775
|
685
|
330
|
1.51-1.55
|
1.13-1.15
|
0.61
|
PII
|
1270
|
1175
|
635
|
310
|
215
|
140
|
120
|
0.53-0.56
|
1.06-1.11
|
|
PIII
|
1365
|
1370
|
1005
|
510
|
380
|
230
|
160
|
0.60-0.69
|
0.99-1.06
|
|
Abt 19 setae on abdominal seg. GpVIII; abt 8-11 on seg. X, which is wider at its widest point (len/gr.wdth. 1.7-2.1), sometimes almost a "half-moon", than in other species of Chironomus. Cercus essentially rectangular although dorsal margin may be curved, longer in the dorso-ventral dimension, with a broad ventral bump.
Pupa: Length of exuviae about 8.4 (7-10) mm, inner margin of wing case (1.3-1.6 mm) about 17.5% of exuvial length. Length of antennal sheath of female about 835 mm. Cephalic tubicles about 155-180 µm long and 130-135 µm wide at base, seta at least 40 µm long.
Respiratory base about 130-140 µm long and and 60-80 µm wide (i.e. about 1.8-2.2 times longer than wide).
Hook row of abdominal segment 2 interrupted into two parts with about 28-33 hooks on each side. Segment width about 970-1063 µm, the total extent of the hook row being 180-202 µm hooks, 100-278 µm gap and a further 180-202 µm hooks.
Fine L-setae present on conjunctives of segs 3/4 and 4/5, often very difficult to see (that of 4/5 at anterior of conjunctive).
Pedes spurii A of segment IV well developed, length (12-13 µm, about 0.17 of the segment length (70-73 µm).
Armature of segments covering most of segment but with a clear spot at mid line of posterior region, larger on the anterior segments.
Posterolateral spur of eighth segment strong and curved with about 5 short spines, and sometimes about 2 small interior spines.
About 69-78 tainiae on each side of the swim fin, mostly in a single row.
Fourth instar larva: A small 8.4 (7-10 mm) yama-type, i.e. no ventral or lateral tubules, anal tubules in a "star"-arrangement (dorsal abt 205 x 75 µm, ventral about 175-210 x 100-110 µm), posterior prolegs about 4 times longer than width at base, terminal hooks either about 139 µm or 63 µm long.
Gula and frontoclypeus slightly dark to dark, sometimes with slight darkening outside the frontoclypeus. This may be a difference between the two localities.
Fig. dClypeal aperture wider at mid-point with a curved ventral border, about 2.5 times longer than width at widest point.
VHL about 233-238 µm, with mentum width about 0.63-0.66 of VHL (149-153 µm).
Distance between the S4 setae about the same, or slightly larger than that between the antennal bases; S5 setae at same level as the dorsal RO.
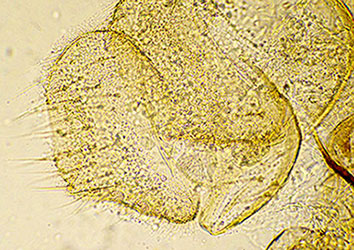
Mentum (Fig. d) of type IV, 4th laterals reduced almost to level of 5th laterals (type i-II); 6th laterals reaching only to base of 5th laterals.
Pecten epipharyngis (Fig. a) with about 11-17 relatively broad teeth. Teeth of premandible (Fig. b) about equal width, the outer tooth slightly shorter.
Ventromental plates (Fig. f) about 3.4-3.8 times longer than deep; separated by about 40% of width of mentum, with about 37-39 striae; VMR about 0.21-0.26, but increasing to about 0.39 near internal end.
Antennae (Fig. c) relatively short, basal segment about 3 times longer than wide, RO up to about a quarter up from base, AR about 2.53-3.11; segment proportions (micron): 103 : 21 : 5 : 6 : 5.
Mandible (Fig. e) of type I-IIB, about 8-9 furrows on outer surface near the base, about 11-12 tainiae in Pecten mandibularis; MTR about 0.31 (0.16-0.42).
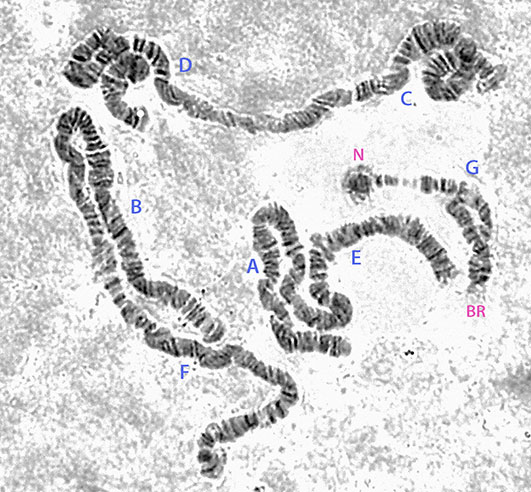
Cytology: Four relatively long thin polytene chromosomes apparently with the pseudothummi-cytocomplex combinationm AE, BF, CD, G. Arm G with a terminal nucleolus and a BR about a third from the other end.
Found in flowing, heavily polluted man-made sewage drains; water quite dark.
Found: India - Manipur: Devchand, Iroisemba, Imphal.
[ Return to Index
| Go to References ]


