C. alpestris Goetghebuer 1934Chironomus nippodorsalis Sasa 1979 (Yamamoto and Hashimoto, unpubl.) - incorrect synonymy. In BOLD Bin: BOLD:AAW4001. Adult: The adults of C. alpestris were well described by Strenzke (1959) as C. dorsalis and C. nippodorsalis was initially described by Sasa (1979), in Japanese. Re-examination of C. nippodorsalis by Yamamoto and Hashimoto in 1976 convinced them that it was indistinguishable from C. dorsalis (personal communication), and hence from C. alpestris. Wing length 3.3 (3.07-3.53) mm. VR 1.08; AR 3.18 (2.96-3.38); LR 1.61 (1.56-1.66); BR 2.4 (2.27-2.53). Ground color of head and thorax grey-yellow, thoracic vittae black, postnotum uniformly black. Legs with tarsal segments dark brown. Thoracic setae: Acrostichals 10.3 (8-13); dorsocentrals 24.4 (21-28); prealar 5.5 (4-8); supra-alar 1.4 (1-2); scutellar 22.9 (19-26). Legs: Lengths (micron) and proportions:
8-10 setae in pale patches (1-2/patch) on tergite IX. Anal point narrow at base; Superior volsella of D(e)-type of Strenzke (1959); Inferior volsella reaching almost to end of anal point or about 1/3 of gonostyle and with simple setae; gonostyle only moderately expanded and narrows over posterior half. 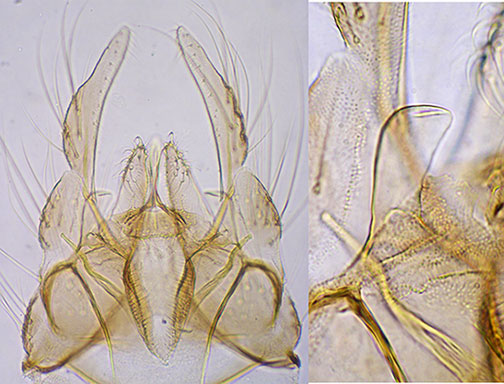 Hypopygium (left) and Superior volsella of C. alpestris. Female: (from Strenzke 1959) Go to C. alpestris immatures The synonymy of C. nippodorsalis with C. dorsalis Strenzke was claimed by Yamamoto and Hashimoto in 1976, and, while this conclusion is supported by the DNA analyses of Kondo et al. (2016) based on K2P distance (i.e. in same BOLD Bin), and Langton and Visser (2003) list this as a synonym of C. dorsalis, there are differences in larval morphology (clypeal chaetae fringed at end, VT of equal length) and cytology that support the recognition of C. nippodorsalis. As well, an analysis of actual base similarity by Dr. Kondo showed 8-10 consistent base differences, while my limited analyses showed no consistent differences, rather a number of unique polymorphisms in each species. Found: Type locality – nr. Garmish-Partenkirchen, Bavaria, GERMANY. Molecular: |
Revised: 27 May 2025
Access: Unrestricted
Copyright © 2020-2025, Jon Martin.