Chironomus c.f. transvaalensis (not Kieffer 1923)The original description of Kieffer along with the basics of Freeman (1957), plus the McLachlan (1969) description of the immatures are available at SEAtransdesc.htm The present species, described below, is a member of this complex, currently known from Israel and Pakistan. A single male from Tivon, Israel was available for examination: AR about 3.4. Frontal tubercles about 56-66 µm long and 3.7-4 times longer than wide. Palpal proportion (µm) 50 ; 47 : 240 ; 235 ; 260+ (shrivelled). Clypeus about 0.69 of the width of the antennal pedicel with 28 setae. Thorax very damaged, so numbers of most setae not clear: acrostichal not seen; at least 16 dorsolaterals; 5 prealar; 2 supa-alar; scutellars in 2 rows, at least 6 in the anterior row and 3 in the posterior row, but total would be much higher. Lengths (microns) and proportions as follows:
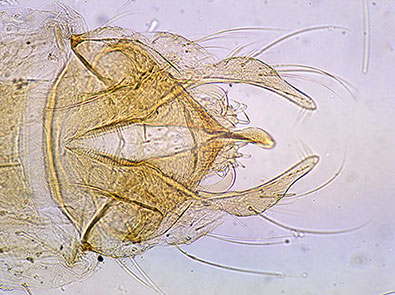 Superior volsella closest to D-type of Strenzke (1959); Inferior volsella reaching part way up the anal point and to basal third of the gonostylus, which is moderately swollen and narrows markedly over the distal half with 4+1-5 setae at the tip. Anal point twisted but appears to be narrower at the base and expanded at the end as noted by Freeman. Adult female and Pupa: Not known Fourth instar larva: Two female larvae were available for study. The larvae were plumosus-type although no metrics were recorded. The anal tubules are not enlarged as in C. transvaalensis, but the ventral pair of one larva were 304 µm long and about 2.5 times longer than wide. Ventral head length (VHL) about 280-320 µm. Cytology: 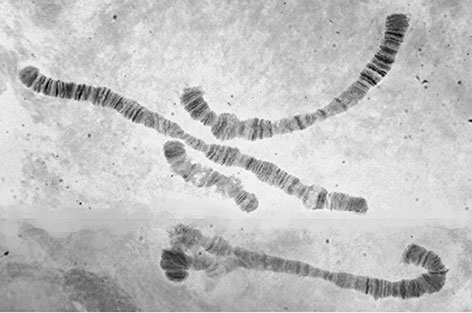 Whole complement of polytene chromosomes of C. c/f transvaalensis from Israel. Four polytene chromosomes with the pseudothummi-arm combination AE, BF, CD, G. The sequences show considerable similarity to those of the African C. transvaalensis: nucleolus sub-terminal in arm C, puff in arm B subterminal with dark bands on distal side, chromosome AE may have a similar banding pattern in the two species, arm A perhaps close to that of C. dorsalis; arm E perhaps similar to C. holomelas. BF may also have similar sequences and CD also appears similar, although there is an inversion around the region of the nucleolus that has not been observed in the African population. The African and the Israel/Pakistan species are obviously closely related but have been isolated for long enough for differentiation of COI sequence and cytology (at least of arm G) to occur. Found: |
Revised: 5 September 2024
Access: Unrestricted
Copyright © 2024, Jon Martin.