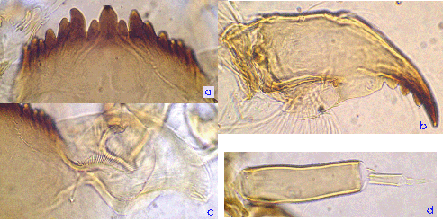
Mouthparts of C. alpestris. Note outward curving 1st lateral of mentum (Fig. a).
Fourth instar larva: (some information from Vallenduuk and Moller-Pillot 2002). A medium plumosus-type larva, with Ventral tubules relatively long and of equal length. Head capsule relatively long and narrow, mentum relatively narrow, mentum width/VHL about 0.49-0.53. Gular region darkened at centre of posterior two thirds, frontoclypeus usually dark but may be lighter, also darkened outside V.
Clypeal chaetae characteristcally fringed at the ends; salivarium about 53-58 µm, and 2.6-7.3 times longer than wide.
Mentum (Fig. a) with 4th laterals reduced to level of 5th (type II-iii); width 44-58 µm. 1st laterals tending to curve outwards; centre trifid tooth with c2 teeth well separated (type III).
Ventromentum (Fig. c) about 282 (255-325) µm wide, separated by about 0.40 of mentum width (IPD) with 39.6 (35-42) striae (Webb et al. 1985).
Pecten epipharyngis with about 12-14 teeth (Webb & Scholl 1985 give 13-16 for Eurpean specimens). Premandible with sharp teeth, inner tooth about 1.5 to 2 times wider than outer tooth (Ty. B1).
Antenna (Fig. d) with basal segment about 3.7 times longer than wide, ring organ about half way up from base; AR about 1.82-2.14, A3 quite short; segment proportions (microns) 123 : 30 : 7 : 11 : 6. (Webb & Scholl, 1985, give slightly different relative lengths, but their measurements are taken from SEM photographs which may give a different view, particularly of segment 1).
Distance between antennal bases may be greater than or about equal to that between the S4 setae.
Mandible (Fig. b) with 3rd inner tooth partly separated and colored (Type IA-IIB); about 18-20 furrows on the outer surface at the base; ; 9-10 taeniae in Pecten mandiularis.

Cytology: Four polytene chromosomes with the pseodothummi arm combination AE, BF, CD, G.
Nucleolus subterminal in arm G, which is closely paired and has three BRs, the largest about a third from the distal end. No nucleolus in other chromosomes.
Chromosomal polymorphism is known only in arm G.
All mapping from Kiknadze et al. 2016 (as C. dorsalis sensu Strenzke with C. alpestris as a synonym). Other studies of the cytology have been made by a number of authors.