Species 2g. C. 'butleri' immaturesFourth instar larva: a medium sized bathophilus-type, but sometimes a melanotus-type with lateral tubules to about 60-280 µm long). Length abt. 13.05 (9.3-20) mm, female; 13.12 (9.4-17.4) mm, male); Ventral tubules may be of fluviatilis-type, with anterior pair usually slightly longer (ant. 1.27 (0.8-1.76) mm; post. 1.22 (0.84-1.96 mm). Anal tubules about 300–560 µm long and about 2-4 times longer than wide, with the dorsal pair sometimes slightly longer than the ventral pair. As well, the longer anal tubules are found in the more northern populations (e.g. Saskatchewan and Kansas) with shorter ones in Mississippi.
Over 2/3 of gular region dark, extending higher at the edges than in the midline and widest anterior to the posterior margin, and frontclypeus pale. Salivary reservoir (below) long, about 92 (63-127 µm), and narrow, about 4.1 (3-4.5) times longer than wide. Mentum (Fig. a) with somewhat rounded teeth; c1 tooth tall and relatively broad, c2 teeth moderately well developed (type IB or III) ; 4th lateral reduced to about level of 5th lateral (type II), although Hilsenhoff & Narf (1968) express that the 5th laterals are raised; 6th laterals generally arising below the level of other teeth.
Ventromental plates (Fig. c), 3.1-4.0 times wider than deep; 1.08 (0.8-1.15) times the mentum width; with about 36.7 (32-42) striae;; Interplate distance (IPD) about a third to a half of the mentum width; VMR 0.29 (0.24-0.33). Pecten epipharyngis (Fig. d), with about 14.7 (12-18) relatively blunt teeth (type B), lateral teeth smaller and narrower. Premandible (below) with inner tooth relatively broad, about 3.5 to 7 times wider than the outer tooth which tapers to a relatively fine tip (type B1). 
Salivary reservoir (at left), Pecten epipharyngis and Premandible of C. 'butleri' Photo courtesy Isabelle Proulx.
Basal segment of antenna (Fig. b) relatively short - only 0.34-0.43 of the Ventral head length, about 3.2 (2.3-3.7 times as long as wide, RO a third to a half up from base of segment; AR 2.34 (2.0-2.6); relative length of segments (micron): 145 : 29 : 8 : 12 : 6.
Distance between antennal bases (143-213 µm) greater than distance between S4 setae (132-200 µm), which are separated by 75-88% of the Frontoclypeal width at that point. S5 setae varying from slightly posterior to slightly anterior of the nearby RO.
Mandible (Fig. e) of type IA to IIB and with about 16.2 (13-22) furrows on the outer surface near the base; Mdt-Mat 31.8 (20-43) and MTR 0.38 (0.25-0.46). The pupa (incl. exuviae of proposed holotype and allotype): Brown cephalothorax and generally pale (yellowish) abdomen. Shagreen over the posterior 3/4-4/5 of TII-V, split into two halves at midline on TV, reduced to a small posterior group on TVI.
Female abt. 9.59 mm (2), male about 9.67-9.75 mm (2), in length. Antennal sheath of female about 885 µm long. Inner margin of wing case 1.64-1.90 mm. Cephalic tubercles large, 114-177 µm long and 1.2x (fem) or 1.65-1.75 (male, Fig. below) longer than wide; with seta at least 48-51 µm long. Obvious frontal wart, about 48-53 µm high and 30-42 µm wide at base. Female antennal sheath abt. 890 µm long. Respiratory scar about 127-170 µm long and HR about 1.7-2.0; respiratory fibers very narrowed at midpoint; a patch with about 3 small vacuoles just anterior.
Hook row of seg. II with about 110 (94-125) hooks, and occupies abt 0.58-0.84 of segment width. Pedes spurii B present on lateral margin of segment 2, not seen on segment 3. Pedes spurii A of segment IV abt 119-245 µm long and 58-119 µm wide, occupying 0.13-0.27 of segment length; that of seg.V of spines about 89-127 µm long and 42 µm wide; seg.VI with small patches of spines. L-seta at junction of segments III/IV at least 76 µm long, that of IV/V not seen.
Caudolateral spur of segment VIII with about 6.8 (4-11) closely applied spines, some arising lower than the head of the spur (see figure below). About 98.3 (84-112 taeniae on margin of swim fin, in 2-3 rows. 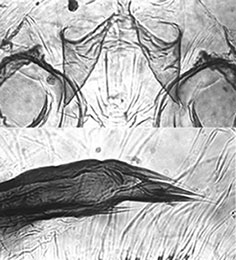
Pupal cephalic tubercles (above) and spur (below) of C. 'butleri' Cytology: 4 polytene chromosomes with the thummi arm combination AB, CD, EF, G; centromeres not heterochromatic.
Arm G usually paired only at the end away from the virtually terminal nucleolus; usually 2 Balbiani rings (BRs) developed - one near the middle, the other near the other end of the arm, but a third may be developed immediately posterior to the nucleolus. No nucleoli in the long chromosomes, but large puff in arm B.
Polymorphism in all arms - polymorphism may be more common in populations in the northeast. butA1: 1a-e,7c-4c, 3i-f, 17a-h, 12c-10, 2c-1f, 15-16, 3e-a, 14-13, 4a-b, 2k-d, 9-7d, 18-19 (Kiknadze)
butA2: Simple inversion
butB1: Puff near distal end of arm, with dark bands proximal (group 8 and 7).
butB2: Complex inversion. Dark bands distal to puff (groups 7 and 8).
butC1: 1a-e, 3c-2f, 4a-6b, 12b-14c, 12a-11d, 6gh, 17a-16, 7d-a, 6f-c, 17b-18, 15-14d, 1f-2e, 8-11c, 19-22 (Kiknadze)
butC2: Inversion of about half the arm towards distal end.
butD1: 1 - 3e, 17 - 18d, 14f - 10d, 14g - 16, 21 - 18e, 10c-a, 7d - 3f, 9 - 7e, 22 - 24 (Kiknadze)
but D2: Inversion of about 1/3 of arm towards distal end.
butE1: 1 - 3e, 5a-e, 10e-c, 3f - 4, 10b - 6a, 10f - 13 inv from bifE1
butF1: 1a-i, 9 - 2, 13c - 17, 10 - 11d, 13b - 11e, 18 - 23 (Kiknadze) inv from bifF1
butF2: Inversion of about 1/3 of arm distal to center.
butG1: Virtually terminal nucleolus, central and distal BRs
butG2: Small inversion distal of the distal BR, apparently rare (MA and MN) [ Return to C. bifurcatus adults, etc.| Go to Index ] |

