Species 5r. Kiefferulus dux (Johannsen, 1905)
Synonyms: Chironomus obscuratus Malloch, 1915 In BOLD Bin: BOLD:AAX0368 Adult: Frontal tubercles not observed, but base 5 µm diameter. Fore tarsis with short, sparse beard (BR abt 2). Pale green. Antennal pedicel ochraceous, flagellum and palps pale brown except at their bases. Thorax ochraceous; legs pale green, brown towards their apices. Thoracic setae: at least 14 acrostichal; 13-14 dorsocentral; 6 prealar; 2 supra alar; 12 scutellar in a single row. 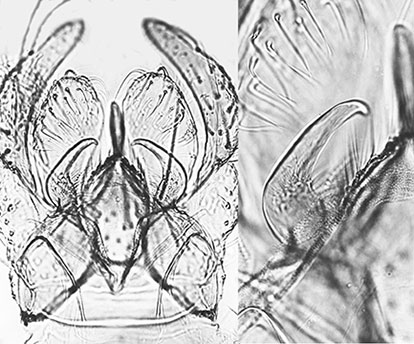 Male hypopygium and superior volsella of K. dux Scattered setae on tergite IX (Townes figures about 9, others 1abt 12-13), some in individual spots, others with 2 in a single spot; anal point short, narrow at base. Inferior volsella broad and rounded at end, and reaches to about distal third of gonostylus (longer than illustrated by Townes,1945 - this may be indicative that more than one species is included under this name, as suggested by Epler (2001). Female: (1 specimen) Color essentially as male. 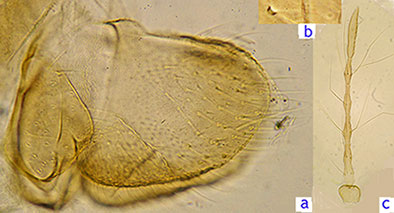 a. Cercus & TX, b. small Frontal tubercle, c. Antenna Wing length 3.52 mm, width 1.02 mm; VR 0.87. Leg lengths (micron) and proportions:
4 setae on GcIX; Seg.X abt 147 x 72 µm, 2.04 times wider than greatest depth, with 11-12 setae. Pupa: Length about 7.15 mm (male), 7.97 mm (female). Female antennal sheath 886 µm long, frontal tubules 20 µm high and 20 µm at base. Shagreen at posterior of segment, divided in midline so that each side is roughly triangular.  Morphology of female pupa of K. dux: a. cephalic tubercles, b. shagreen of TIII; c. spur. Fourth instar larva: A typical Kiefferulus larva with only one pair of ventral tubules. Head capsule somewhat flatter and broader than a typical Chironomus larva. Gula and fronto-clypeus pale, although some darkening at posterior of frontoclypeus. Salivary reservoir firmly attached to ls-2, about 73 (66-78) µm wide and 18.5 (18-20) µm deep. Mentum (Fig. d, below) with 15 teeth, center trifid tooth closer to type IB but c1 tooth broader (damaged in figure below), lateral teeth in an even slope. Ventromentum (Fig. e, below) with anterior margin crenulate, 230 µm wide and about 4.5 times wider than deep with about 66-67 striae which show a substantial fold close to their posterior origin; median margin more sharply turned down than in other studied species. The characteristics of the VM were detailed on the basis of SEM photographs by Cranston et al. (1990). These scans show that, unlike the other studied Kiefferulus species, the striae are divided. Premandible (Fig. b, below) with 6 teeth, typical of the genus, although the small 6th tooth may be difficult to see amongst the thick setal brush. Pecten epipharyngis (Fig. a, below)with about 24 irregular teeth. Antenna (Fig. c, below) proportions (units) 67 : 25 : 13 : 12 : 5, i.e segments 3 and 4 subequeal, A1 about 3.5 times longer than wide, AR about 1.2. Mandible (Fig. f, below) essentially as a type IIIC of Chironomus, lacking furrows, about 13 taeniae in Pecten mandibularis, MTR about 0.38 (0.36-0.42). 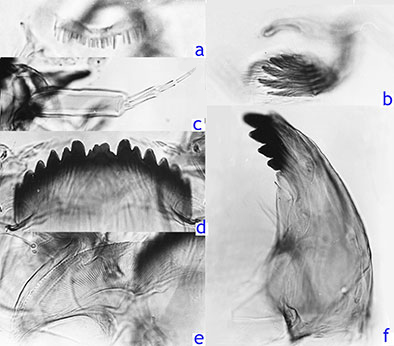 Mouthparts of K. dux larva: a. Pecten epipharyngis, b. Premandible, c. Antenna, d. Mentum, e. Ventromentum, f. Mandible Cytology: Four polytene chromosomes. The pattern does not allow comparison with the arms of Chironomus, other than the smallest chromosome (below) which seems to be the homolog of arm G as it contains the nucleolus and at least two Balbiani rings. At least one polymorphic complex inversion was observed on chromosome I (at Madison, WI) and simple inversions on IIL (at Dunrobin, ONT) and chromosome IV (at Madison, WI). Found: Ontario - Copanspin Farm, Dunrobin (45.42°N, 75.87°W), Carleton Co.; Bear Creek 1 km Carlsbad Springs (45.37°N, 75.47°W); Lake Opeongo (Townes) An apparently widespread species, but it needs to be clarified whether there is more than one species included and, if so, how they are distrubuted. Only one specimen is currently in the BOLD database, and the nearest neighbor is another recognised species of Kiefferulus, so provides no evidence of the existence of multiple species. Epler (2005) suggests the presence of an additional species of Kiefferulus and of Wirthiella in the Southeast: |
Created: 23 January 2025
Access: Unrestricted
Copyright © 2021-25, Jon Martin.