Chironomus "orientalis"This type was identified as C. flaviplumus from the Yangtze River basin in China by Chen and Zhang (GenBank 2015 - unpubl.), for which only the DNA BARCODE sequence is available. Limited information on the larva was available from Thailand (Pramual et al. 2016). Adults: 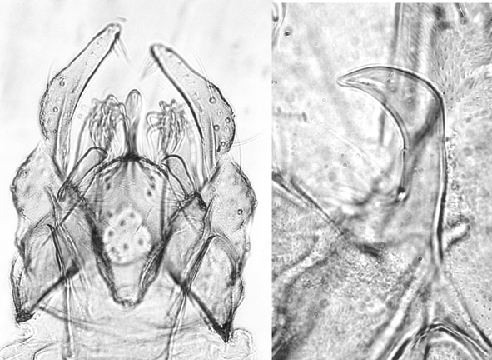 Males Frontal tubercles about 33 - 39 µm, and about 3 times longer than wide. Palp proportions (micron): 44 : 53 : 189 : 222 : 315 Wing length: 2.85 - 3.15 mm; wing width 0.30 - 0.67 mm. VR about 1.02-1.07; abt 2-4 SCf on brachiolum; 9-14 setae in squamal fringe. Thoracic setae - achrostichal about 12-18; dorsocentral about 13-18; prealar about 4-6; supra alar 1; scutellar in 2 approximate rows, 6-7 in anterior row, 11-17 in posterior row. Leg pale; lengths (micron) and proportions as follows:
The superior volsella is essentially a D(e)-type of Strenzke (1959), although often of a beaked type not illustrated by Strenzke (1959), i.e. it varies between a D- and an almost S-type. Setae on 9th tergite: 9 - 12; some setae on inferior volsellae with a simple or trifid fork; gonostylus reduces fairly quickly over posterior half. Female: Leg proportions (micron)
ant Ta4/Ti about 0.98; Ta3 and Ta4 subequal in length. Differences from other members of the C. samoensis/flaviplumus group: Pupa: Exuviae length about 7.2-7.8 mm; inner margin of wing case 1.42-1,45 mm. Cephalic tubercles (see below) variable, length from 23-121 µm, with subterminal setae about 60 µm long. 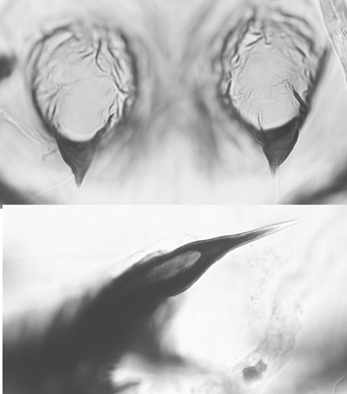 Larva: a medium sized plumosus-type larva (length about 10.7-14.3 mm, lab. reared). Anterior ventral tubercles (1.24-1.84 mm) shorter than posterior pair (1.40 - 2.28 mm). Cytology: 4 polytene chromosomes with the pseudothummi arm combination AE, BF, CD, G. Molecular Sequence: Found: China - Yangtze River basin (30.09°N, 115.12°E) (GeneBank) Indian specimens described by Chattopadhyuy et al. (1991), are not the same species and one has been renamed C. indiaensis (Martin 2011b), while others are the widespread species PK2. May be able to be bred in the laboratory. |
2 March 2019
Access: Unrestricted
Copyright © 2005-2019, Jon Martin.