| Fe
| Ti
| Ta1
| Ta2
| Ta3
| Ta4
| Ta5
| LR
| F/T
| BR
|
PI
| 1420
| 1380
| 2040
| 1000
| 820
| 720
| 320
| 1.47
| 1.02
| 2.2
|
PII
| 1420
| 1440
| 820
| 550
| 380
| 270
| 180
| 0.57
| 0.99
|
|
PIII
| 1640
| 1780
| 1320
| 820
| 560
| 340
| 200
| 0.74
| 0.92
|
|
No sensilla chaetica seen on mid Ta1, only 2 on hind Ta1
Note mid tibia is as long, or slightly longer than the femur
Most setae on fore Ta1 about 2.2 times diameter of Ta1, with a few longer.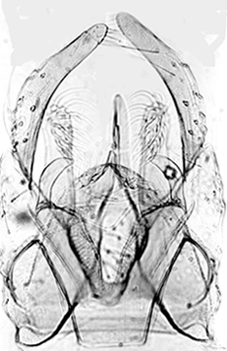
Hypopygium of C. sp. 4s.Abdominal tergites with brownish black band covering at least the anterior 2/3 of segment, whitish in posterior region.
TIX with about 9 setae apparently in individual spots.
The anal point is relatively fine, styles are slender, tapering over the posterior half, and the superior volsella is most similar to D(e)-type of Strenzke (1959), but is not dark as in C. tenuistylus. Inferior volsella reaching about to end of anal point and the middle of the gonostylus.Pupa: from a male exuvia: Length about 8.7 mm; inner margin of wing case about 1.8 mm.
Cephalic tubercles about 105 µm long, 78 µm wide at base, with a subapical seta about 38 µm long.
Abdomen with a central patch of shagreen on segments II-V, grading from posterior 2/3 on seg. II, to whole length of segment on segment V; on segment VI the shagreen is restricted to the anterior third.
Pedes spurii B and A are as usual for the genus. Numbers of L-setae on segments II-IV also as usual, the posterior two on segment IV arising very close to each other.
Hook row on segment II with about 78 hooks, occupying about 40% of width of segment. Caudolateral spur of segment VIII with 1 or 2 spines.
About 72 taeniae, posteriorly in two rows, on each side of anal lobe.
Larva: A small plumosus-type larva, length about 8.8-11.2 mm (fem. 11.0-11.2 mm; males 8.8-9.7 mm); lateral tubules (200-280 µm), ventral tubules with anterior pair usually longer (ant. 0.84-1.12 mm; post. 0.80-1.16 mm). Anal tubules relatively long (3.2-4.6 times longer than wide), posterior pair usually longer and thinner (3.7-4.6).
Gula slightly darkened on posterior third, frontoclypeus pale to dark, often with a stripe along the outer margin.
Mentum (Fig, c)with sharp teeth; 4th lateral slightly reduced compared to the 3rd and 5th laterals (type I-II); central trifid teeth with c1 tall and linear in outline, the c2 teeth well developed (type III).
Ventromental plates (Fig. e) separated by about 0.2-0.35 of mentum width, with about 39-40 striae that extend at least 2/3 of way to anterior margin; VMR 0.32-0.35.
Pecten epipharyngis (Fig. b) with about 11 or 12 sharp teeth. Premandible (Fig. a) of type B2 with inner tooth at least 4.5-5x the width of the outer, coming to fine points.
Antenna (Fig. d) with basal segment relatively long, and slightly curved, about 3.7-4.3 times longer than wide, and 3.3-3.7 times longer than segment A2; RO between 0.33 and 0.5 up from base of segment; AR about 1.8-1.65; segment proportions (micron): 129 : 36 : 10 : 13 : 8.
Distance between the antennal bases greater than the distance between the S4 bristles on the frontoclypeus.
Mandible (Fig. f) with 3rd inner tooth sometimes pale and hardly developed, but in others partly to well developed and grading in coloration (type IA-IIIC).
Cytology: 4 polytene chromosomes with the thummi-cytocomplex arm combination AB, CD, EF, G.
Nucleolus only in arm G, virtually terminal, but a heterochromatic cap visible in some specimens; two Balbiani rings, one distal, the other just distal of middle of the arm. Another possible BR, or a puff, proximal in arm B.
Centromeres not heterochromatic.
Polymorphism at least in arm F, and F2 may carry the male determiner (MD).
Arm A1: 1 - 2c; 10 - 12, 3 - 2d; 9 - 4; 13 - 19 i.e. as holomelas, tenuistylus, longistylus, etc.
Arm B1: BR or puff just distal to characteristic bands (25 - 27), which are in the usual position near the centromere.
Arm E1: 1 - 3e, 5 - 10b, 4 - 3f; 10c - 13 i.e. as tenuistylus, etc.
Arm F1: possibly Standard, i.e. 1 - 23, i.e. as longistylus, etc. Homozygous in females.
Arm F2: simple inversion of at least middle half of the arm, possibly In17-11, i.e. as tenuistylus. Heterozygous in males.
Arm G1: middle of arm rearranged compared with C. tenuistylus
Found: Wisconsin - Why Not Bog Lake, County Road N, Vilas Co (46.02; -89.62).
Known specimens were reared from two egg masses at the edge of a bog lake.
Although the adult appears similar to C. tenuistylus, the cytology makes it clear that this is a different, but probably related species. Arms A, E, and F have similar sequences, but arms B, C, D, and G show differences that cannot be explained by simple inversions.
[ Return to Index| Go to References ]