Species t. C. dilutus immatures. Pupa: (from Shobanov et al. 1999) Exuvia pale-brown; thorax may be darker. Shagreen: trapezoidal spine patches, wider towards posterior margin in TII & III, becoming narrower in posterior 1/4 of TIV-V, and a pale line on the mid line of TV-VII; groups of small spines on TVII & VIII. Antennal sheath 1.89 (1.74-2.04), wing sheath 2.80 (2.53-3.16), abdomen length 9.51 (8.2-10.7), no. of hooklets on tergite II, 92 (67-113); anal spur dark or black-brown with about 4-5 appressed spines at tip and a smaller spine on one side near the base.
To this can be added: Total length 12-12.8 mm (male); CT 80-120 µm high, 65-74.5 µm wide at base; hooklet row of segment II covers about a third to a half of the segment width. The L-setae at the TIII/IV conjunctive are about 125 µm long, those at the TIV/V conjunctive at least 100µm long.
Pedes spurii B are present on segments II and III, and a large Pedes spurii A, about 315-340 µm long and 1.5-2.3 times longer than wide, which cover about a quarter of the length of segment IV; the PSA of segments V and VI are patches of spines, about 150-250 µm long on segment V and 115-125 µm long on segment VI. The number of appressed spines on the spur of segment VIII is 5.5 (3+1-7), with the higher numbers from pupae of the Eastern race (below). The number of flattened taeniae on each side of the anal lobe is about 152-165 in up to 3 rows, particularly towards the distal end. 
Spur of pupa of the Eastern race of C. dilutus. Fourth instar larva: A large plumosus-type. As indicated above, larvae of the Eastern race (fem. 23.22 mm; 14.8-28.9; male 19.96 mm; 16.9-24.2) are larger than those of the Western Race (fem. 21.6 mm; 19.8-25.9; male 17.96 mm; 15.3-21.5). Lateral tubules long (longer in the Western Race), up to 1/3 of segment length (617.5 µm; 310-1070); Ventral tubules longer than posterior parapods, posterior pair generally longer (ant. 2.20 mm; 0.80-3.84; post. 2.35 mm; 1.29-3.94). Anal tubules well developed, dorsal 425-730 µm, ventral 506-650 µm and about 2-3 times longer than wide. Gular region pale or slightly darkened on posterior third to half and wider than the mentum, with frontoclypeus darkened particularly in the center, posteriorly. Salivary reservoir about 2.9-3.4 times longer than wide. 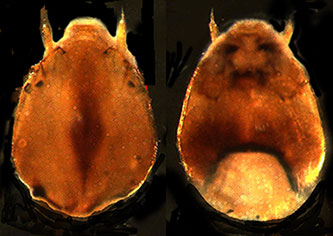
Frontoclypeus (left) and gula (right) of C. dilutus. Photo courtesy of I. Proulx." Mentum with rounded teeth; c1 tooth broad with short parallel sides, c2 teeth quite well separated (Type II); 4th laterals only slightly reduced (type I). Ventromental plates separated by about 35% of the mentum width, each with about 5 -66 striae.
Pecten epipharyngis with about 10-18 broadly rounded or flat teeth (Hilsenhoff & Narf 1968, Shobanov et al. 1999). Premandible (below) with moderately broad teeth, inner tooth about 3-5 times wider than outer tooth, coming to a broad point (Type C).
Basal segment of antenna about 3.7 times longer than wide; AR 2.1 (1.79-2.29). Mandible of type II, variation of 3rd inner tooth shown in Figs 4L and M of S of Shobanov et al. (1999), about 19-25 furrows on outer surface near the base. Note that female larvae can be larger than the 25 mm limit indicated by Shobanov et al. (1999). 
Premandible of C. dilutus. Cytology: 4 polytene chromosomes with the camptochironomus arm combination AB, DE, CF, G.
Arm G with 3 Balbiani rings but no nucleolus. Position of Balbiani rings variable due to the polymorphisms; arms B and C with a nucleolus near the centromere, nucleolus also in arm D with an extra band.
Chromosome polymorphism in all arms, with 23 sequences known.
The male sex determiner is on arm C near the centromere, but the female sex determiner reported by Thompson (1971) does not actually exist (Martin and Lee 1984).
dil n'A1: 1a-b, 8c-7b, 3i-7a, 1g-c, 8de, 17-13, 1h-2c, 9c-8f, 10-9d, 11-12, 3h-2d, 17g-19
dil n'A2:
dil n'B1:
dil n'B2:
dil n'B3:
dil n'C1: 1-2d, 4g-6b, 9-11c,3c-2e, 11d-14c, 19-16, 7d-a, 6h-c,8, 15-14d,4a-f, 20-22
dil n'C2:
dil n'D1: 1-2b, 15-14, 10, 4-7, 2c-3, 13, 22-18e, 8-9,17-18d, 12-11, 16e-a, 23-24 as pD1, except for nucleolus and extra band in 10B
dil n'D2: as pD2?, except for nucleolus and extra band in 10B
dil n'D3:
dil h'E1: 1-2b, 7h-8, 9-10b, 3e-2c, 7g-3f, 10c-13
dil h'E2:
dil n'E3: 1 - 2b, 10a-c, 3f - 7g, 2c - 3e, 10b - 7h, 11 - 13
dil n'F1: 1 2, 7-9, 16, 6-3, 15-10, 17-23; as pF3 in Europe
dil n'F2:
dil n'F3: 1a-d, 9b-12, 3b-2, 13a-d, 1i-e, 3c-5c, 16-14d, 7-9a, 6-5d, 14c-a, 2a-e, 17-23
dil n'F4:
dil h'G1: BR1 and BR2 separated by about 1/3 of length, towards the centromeric end.
dil h'G2: Inversion of virtually the whole arm, so the close BRs are now at the distal end.
dil n'G3: Inversion including BR2, so that BR1 and BR2 are separated by over half the chromosome length.
dil n'G4: Reported by Acton (1962) as rare, but limits not defined. Martin et al. (2010) provided a physical map for the position of some genes on the polytene chromosomes.
[ Return to Index| Go to C. dilutus adults ] |


