Species x. C. hyperboreus Staeger, 1845 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Townes shows about 11 setae in a number of pale patches on TIX. Anal point narrow, extending beyond midpoint of gonostyle; Superior volsella rather unusual, not easily fitted into the Strenzke groups, closest to E(i) but more curved and of similar width up to its distal end. Inferior volsella not reaching to end of anal point, but to about midpoint of gonostylus.
Female:

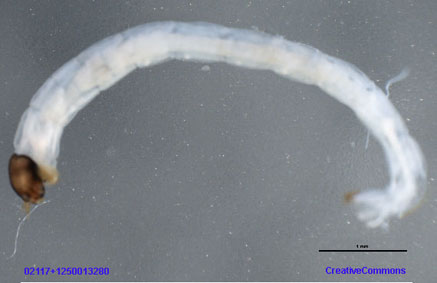
From a photograph in the BOLD database (above), the following characters can be adduced:
Wing length about 3.1 mm.
Thorax, scutellum, etc, blackish, abdominal segmets blackish at base, with a brownish band across the distal ¼ to 1/3; bases of anterior and midlegs brownish, rest of legs blackish.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Pupa: no information available, although described by Andersen (1937).
Larva: a medium sized (male 13.3 (12.2-14.5) mm) salinarius-type. Anal tubules relatively long (dorsal 375x140, ventral 401x185 µm), dorsal about 3 times longer than wide, the ventral pair about 2.2 times longer. Head capsule brown rather than yellowish.
Gular region, frontoclypeus (FC) and sometimes other parts of the head, dark brown; gula darkening over posterior half, wider than the mentum, anterior margin rounded, and more extensive at lateral edges. Salivary reservoir about 61-79 x 18-25 ݙm (l/w 3.1-3.5).
Ventromentum (Fig. e) abt 194-205 µm; wide and abt 3.15 (3.1-3.3) times wider than deep; slightly narrower shorter or the same width as mentum; abt 42-44 striae; VMR about 0.24-0.28.
Pecten epipharyngis (Fig. a) with 8-14 teeth, sometimes (Fig. b) irregular and broad.
Premandible with broad teeth about equal in length; inner tooth about 3-4 times wider than outer tooth, coming to relatively broad point (Ty. B2).
Antenna (Fig. c) with basal segment about 3.15 (3.1-3.3) times longer than wide, RO about 0.35-0.40 up from base; AR about 1.80 (1.66-1.94); A2 about 0.29-0.32 of A1; segment proportions (micron) 126 : 37 : 10.5 : 14 : 7.5.
Distance between antennal bases about the same as the distance between the S4 setae, which are separated by about 0.78 of the FC width.
Mandible (Fig. e) abt 245-266 µm long, with 3rd inner tooth usually well developed (type IIIA-B), but may be broken, and with about 14.8 (14-16) furrows on the outer surface near the base, Pecten mandibularis abt 13-14; Mdt-Mat abt 19.3 (25-28) µm, MTR 0.23 (0.19-0.28).
Cytology: 4 short polytene chromosomes with the thummi arm combination AB, CD, EF, G, but Keyl pattern hard to recognise.
Centromeres heavily heterochromatic, often forming a chromocentre.
Arm G short, often unpaired, with a nucleolus near the centromere and possibly a Balbiani ring near the other end.
Polymorphic in arm A. Polymorphism also occurs in arm F, but only F2 is present at Ellesmere.
hypA1: 1 - 2c, 10 - 12, 3 - 2d, 9 - 4, 13 - 19 ie. as holomelas A1
hypA2: 1 - 2c, 10 - 12, 7 - 9, 2d - 3, 6 - 4, 13 - 19 (Greenland)
hypA3: 1 - 2c, 3 - 2d, 9 - 7, 12 - 10, 6 - 4, 13 - 19 (Ellesmere)
hypB1: as riihimakiensis
hypC1: 1-2c, 3-2d, 9-7, 12-10, 6-4, 13-19 (Wülker) or
1-6b, 11c-8, 15-11d, 6gh, 17a, 16h-a, 7d-a, 6f-c, 17b-22 (Kiknadze)
hypD1: 1 - 3, 11 - 18d, 7 - 4, 10 - 7e, 18g - 24 ie. as longistylus, tenuistylus, etc.
hypE1: 1 - 3e, 7 - 5, 8 - 10b, 4 - 3f, 10c - 13
hypF1: 1 - 6, 12 - 7, 13 - 23 (Greenland)
hypF2: 1 - 2, 14 - 13, 7 - 12, 6 - 3, 15 - 23
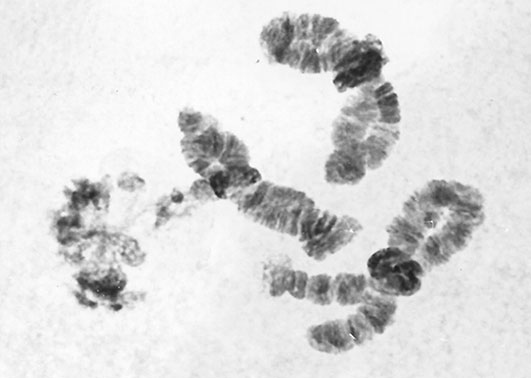
Polytene chromosome complement from Hazen Camp Pond, Ellesmere Island, N.W.T.
Found: Alberta - NE Jasper Lake, Jasper National Park (53.192°N -117.954°W). (as sp. TE13)(BOLD)
Manitoba - Launch Rd Bluffs, Churchill (58.765°N. -94.013°W). (as sp. TE13) (BOLD)
Nunavut (formerly North West Territories) - Hazen Camp Pond, Skeleton Lake, and its inlet marsh, Hazen, Ellesmere Island
(Oliver & Corbet, 1966).
Alaska - Point Barrow (Butler et al. 1980)
Greenland - Egedesminde (now Aasiaat)(68.71°N, 52.87°W) (Townes 1945); Lake 517, Stoe Kvaneso, Western Greenland
(Type locality); Ilimaussaq intrusion, South Greenland (60-61°N, 45-46°W) (Wülker & Butler 1983); Nedre Midsommer Sö, Peary Land
(82.63°N, 32.50°W); Zackenberg Research Station, Northeast Greenland (GenBank).
Arctic lakes and pools.
Chromosomes pictured and briefly described by Wülker & Butler (1983), redescribed by Wülker & Martin (2000).
Molecular sequences:
mtCOI: A number of sequences are available in GenBank or BOLD, under the names C. hyperboreus or C. sp. TE13 (from Arctic Canada).
Modified: 2 October 2025
Access: Unrestricted
Copyright © 2000-2025, Jon Martin.
