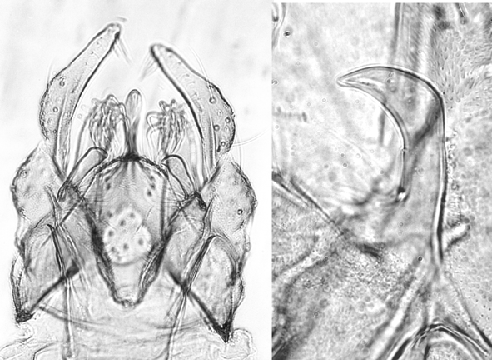
Female
| Fe
| Ti
| Ta1
| Ta2
| Ta3
| Ta4
| Ta5
| LR
| F/T
| Ta4/Ti
|
PI
| 1640
| 1180
| 2290
| 1347
| 1102
| 1112
| 410
| 1.91-1.92
| 1.37-1.42
| 0.90-0.97
|
PII
| 1565
| 1400
| 828
| 438
| 309
| 192
| 143
| 0.58-0.61
| 1.11-1.14
| -
|
PIII
| 1703
| 1640
| 1322
| 695
| 544
| 311
| 185
| 0.79-0.82
| 1.02-1.06
| -
|
ant Ta4/Ti about 0.98; Ta3 and Ta4 subequal in length.Abdomen pale, probably greenish; about 4 setae on gonopophysis VIII.Differences from other members of the C. samoensis/flaviplumus group:
Important features of males are the AR of 2.4-2.9 (lower than that of C. flaviplumus, but similar to C. samoensis), LR of about 1.8-2.0 and fore Ta5, which is about 0.35-0.4 length of Ti.
In the female the fore legs are very long, with LR about 1.9, and Ta3 and Ta4 are about equal in length, only a little shorter than Ta2, ratio Ta4/Ti about 0.98
See here for descriptions of C. samoensis Edwards.
Pupa: (5 males) Exuvia length about 7.4 (7.2-7.8) mm; inner margin of wing case 1.8 (1.42-2.81) mm. Cephalic tubercles (see below) variable, length from 23-38 µm, slightly less than base width; with subterminal setae about 64 (56-75) µm long; no indication of frontal warts. Basal ring of respiratory horn kidney shaped, about 131 (130-137) µm long and 64 (56-68) µm wide, HR 2.0-2.2.
Small Pedes spurii B and about 74 (68-85) recurved hooks on abdominal segment II; well developed Pedes spurii A on segment IV, about 86-166 µm long and 61-93 µm wide (l/w 1.4-2.8) and about 0.20 (0.18-0.26) of the segment length. Caudolateral spur (see below) of segment VIII on an elongated base with narrowed (paler) center, with 1.8 (1, 2 or sometimes 3) spines, the additional spines reduced in size. Anal fringe with about 76 (44-100) taeniae initially in a single row, but increasing to two, or sometimes 3, rows at distal end.
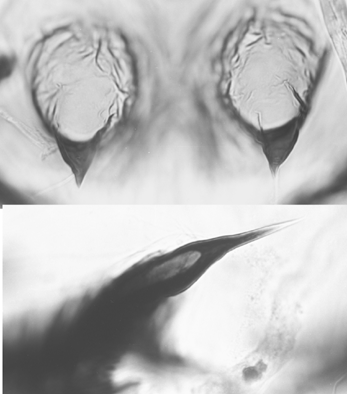
C. "orientalis": Cephalic tubercles (above) and caudolateral spur of segment VIII (below)Fourth instar larva: a medium sized plumosus-type larva (length: females about 11.8 (9.0-14.3), males 10.9 (9.2-11)(male) mm. (lab. reared). Lateral tubules generally shorter in females (250 (200-360)) µm, than in males (347 (340-360)) µm. Ventral tubules longer in females than males, anterior pair 1.49 (1.24-1.84 mm.), shorter than posterior pair 1.72 (1.40-2.48) mm. Anal tubules variable between localities.
Gula pale or very slightly darkened on posterior third; frontoclypeus pale to dark. Clypeal aperture about 3.64 (2.60-4.43) times longer than wide.
Mentum (Fig. b) with square sharp teeth, c2 teeth of central trifid tooth well separated from c1 tooth (type IB), 4th laterals slightly to moderately reduced (type I-ii); about 0.53-0.59 times the ventral head length.
Ventromentum (Fig. c) about 183 (180-185) µm wide and 3.87 (3.72-4.05) times wider than deep, with about 34.2 (31-38) striae; VMR about 0.29 (0.25-0.32); about 1.17 (1.13-1.22) times the mentum width.
Pecten epipharyngis (Fig. a) with about 16-21 variable but sharp teeth which become smaller at the ends. Premandible (Fig. b) with inner tooth about 2.3-3.6 times wider than the outer, coming to a relatively narrow point (Ty. B2).
Distance between the antennal bases slightly larger, 143.8 (127-157), than the distance between the S4 setae, 136.6 (124-144), which are separated by about 0.82-0.87 of the width of the mentum at that point.
Antenna (Fig. d) with a moderately long basal segment, which is about 3.74 (3.62-4.03) times as long as wide; AR about 1.87 (1.62-2.05). Antennal proportions: 115 : 34: 9 : 12 : 8.
Mandible (Fig. e) with third inner tooth only slightly darkened (Type IA/B), and with about 13.1 (12-14) furrows on outer surface near the base; MTR about 0.35 (0.32-0.38); 11.8 (10-13) taeniae in Pecten mandibularis.
Cytology: 4 polytene chromosomes with the pseudothummi arm combination AE, BF, CD, G.
Nucleolus virtually terminal in arm G; well developed BR about one third from the other end, and a smaller BR close to this other end; closely paired. No nucleolus in long chromosomes.
Arm A differs from that of C. flaviplumus by a complex inversion, and arm F by possibly a simple inversion. Irradiation experiments indicated only that the MD region was not on the CD chromosome.
"orl"A1: 1 - 2c, 10 - 12, 3 - 2d, 9 - 4, 13 - 19 as holomelas
"orl"B1: Puff of group 7 just distal to the middle of the arm with dark bands distal of it.
"orl"C1: Characteristic groups 3-4 about one third from distal end of the arm.
"orl"D1:
"orl"E1: 1 - 3e, 10b - 3f, 10c - 13 as aprilinus, etc.
"orl"F1: (possibly) 1 - 2a, 10a-d, 15 - 14e, 9 - 2b, 11 - 14d, 16 - 23 In14d-9 from flaviplumus
"orl"G1: Subterminal nucleolus, median and distal BRs.
Molecular Sequence:
CO1 - GenBank accession nos. for Chinese specimens are KP902730-31 and for Thailand KT213029-038. In BOLD they have 99.5% similarity to an early release sequence named as ChironomidaeGC sp. 7 from Queensland, Australia.
Found: China - Yangtze River basin (30.09°N, 115.12°E) (GeneBank, as C. flaviplumus)
Bangladesh - Chittagong (22.4685°N, 91.7808°E)(BOLD)
Malaysia - Botanical Gardens, Univ. Malaya, Selangor (3.1295°N, 101.656°E)(BOLD)
Thailand - Mahasarakham University (16.242°N, 103.260°E), and Ban Keab (16.250°N, 103.210°E), Kantharawichai Dist.,
Maha Sarakham; Ban Tha Reu (15.303°N, 103.392°E), Satuek Dist. Buri Ram (15.30°N, 103.38°E).
Widespread in the Orient.
Also in Australia - Northern Territory & Queensland.
Proposed type series: Holotype male: Radon Creek, Kakadu National Park ANT.15.3 Egg mass #3, reared male 3. Allotype female: details as holotype, female 1.
Differences from other members of the C. samoensis/flaviplumus group:
Important features of males are the AR of 2.4-2.9 (lower than that of C. flaviplumus, but similar to C. samoensis), the LR of about 1.8-2.0 and fore Ta5, which is about 0.35-0.4 length of Ti. In the female the fore legs are very long, with LR about 1.9, and Ta3 and Ta4 are about equal in length, only a little shorter than Ta2, and Ta5 about a third of the length of the Ti.
The species is probably most closely related to the Japanese C. flaviplumus Tokunaga.
Aspects of the relationships between some of the members of this group, from a molecular perspective, are given by Pramual et al. (2016).Material identified as C. samoensis from India is also cytologically distinct, one species has been renamed Chironomus indiaensis (Martin 2011b), and others are the widespread species PK2.
This species can be bred in the laboratory, as fertile egg masses were obtained from adults reared from wild collected larvae in Australia. The related Japanese species has also been maintained in a laboratory culture (Elbetieha and Kalthoff 1988).See also C. flaviplumus, C. circumdatus, C. indiaensis, C. nr. flaviplumus.[ Go to Index | Return to C. flaviplumus ]